Development of PBL-based teaching modules to improve the mathematical communication skills of phase D class VII students
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31629/jg.v9i2.7507Keywords:
PLSV & PtLSV, mathematical communication skills, problem-based learning modelAbstract
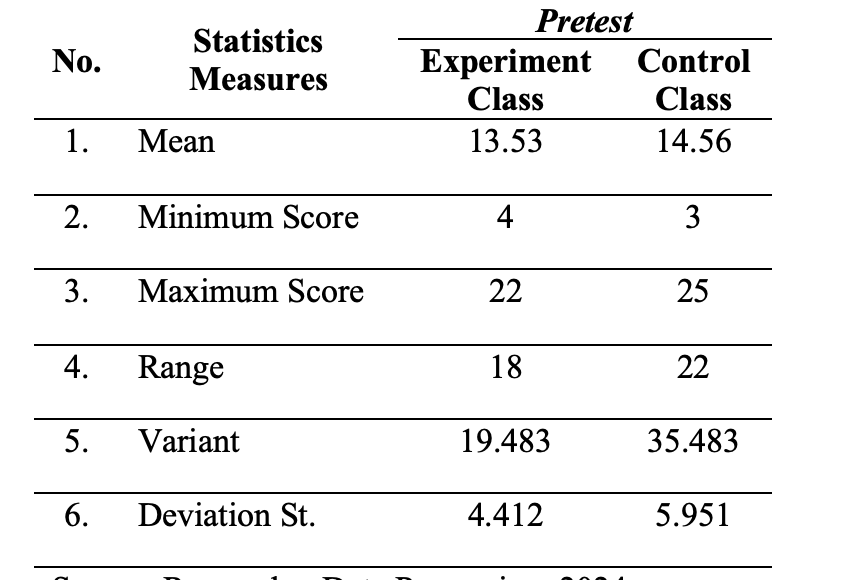
This study aims to develop a product in the form of a mathematics teaching module based on the Problem-Based Learning (PBL) model to enhance students' mathematical communication skills in the context of linear equations and inequalities with one variable for Grade VII students in junior high schools (SMP/MTs). The study evaluates the teaching module's validity, practicality, and effectiveness. Additionally, the findings of this research can serve as a reference for teachers in designing teaching modules that improve communication skills in other mathematical topics and as a resource for students to practice and enhance their communication skills. This research is based on the importance of mathematical communication skills for students. According to the Ministry of National Education, one of the objectives of mathematics learning is to enable students to communicate their ideas through symbols, tables, diagrams, or other representations. However, field observations show that the reality is quite the opposite. The mathematical communication skills of Grade VII students (Phase D) in junior high schools are still relatively low, particularly in linear equations and inequalities with one variable. One of the indicators of this issue is that students do not create mathematical symbols accurately when solving problems. While they can solve problems presented in a format like the teacher's examples, they struggle with different problem formats, especially word problems, which are confusing. The data collection instruments used in this study include validation and practicality instruments. The data collection techniques involve interviews, questionnaires, and mathematical communication skill tests. The data analysis techniques employed are both quantitative and qualitative analyses. The development of the teaching module in this research follows the 4-D model (Four-D Model), which consists of four stages: defining, designing, developing, and disseminating.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Jurnal Gantang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.