Student errors in solving exponent problems: A qualitative Newman’s procedure analysis among Indonesian senior high school students
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31629/dsx7ad32Keywords:
error analysis, Newman procedure, exponent, mathematics education, problem solvingAbstract
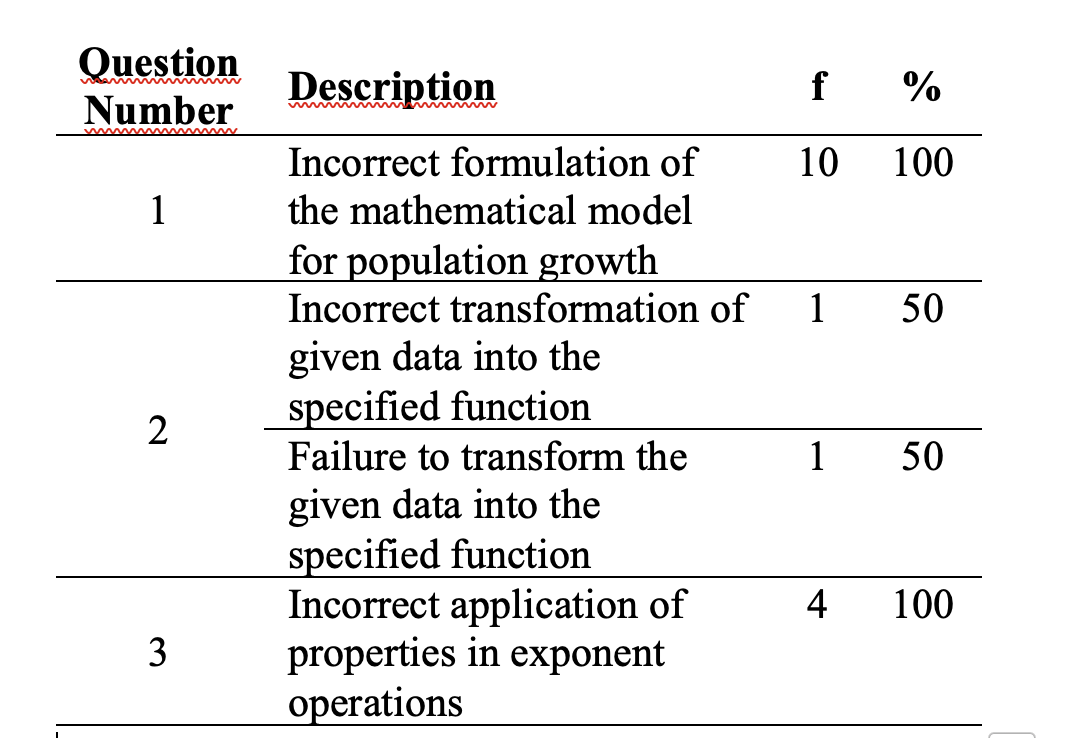
Exponents constitute a fundamental concept essential for understanding advanced mathematical topics such as logarithms, geometric sequences, and compound interest. However, many students continue to experience difficulties in solving exponent-related problems. This qualitative descriptive study aims to analyze the types of errors made by tenth-grade students when solving exponent problems using Newman’s procedure and to investigate the factors contributing to these errors. The participants were 23 students from Madrasah Aliyah Negeri (MAN) Insan Cendekia Siak in the 2024/2025 academic year. Data were collected through written tests and interviews, then analyzed by organizing and categorizing students’ errors according to Newman’s five stages. The results show that 12% of students committed reading errors due to inaccuracies in interpreting the questions, while no comprehension errors were identified. Transformation errors were the most common (49%), primarily due to students’ difficulties in constructing appropriate mathematical models. Process skill errors accounted for 21%, primarily due to computational mistakes, and encoding errors represented 18%, arising from students’ inability to use the provided information effectively. These findings deepen the understanding of students’ patterns of error in exponent problems and imply the need for more targeted instructional strategies, especially those that strengthen mathematical modeling and procedural accuracy.
Downloads
References
Anggraini, D., & Siregar, R. M. R. (2020). Analisis kesalahan siswa dalam menyelesaikan soal eksponen melalui pembelajaran online di masa pandemi kelas X SMA Swasta Tamansiswa Binjai. Serunai: Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu Pendidikan, 6(2), 86–91. https://doi.org/10.37755/sjip.v6i2.331
Annisa, A., Prayitno, S., Kurniati, N., & Amrullah, A. (2021). Analisis kesalahan dalam menyelesaikan soal cerita matematika materi relasi dan fungsi berdasarkan prosedur Newman ditinjau dari perbedaan gender pada siswa kelas VIII SMP Negeri 22 Mataram tahun pelajaran 2021/2022. Jurnal Ilmiah Profesi Pendidikan, 8(1), 323–334. https://doi.org/10.29303/jipp.v8i1.1141
Baroody, A. J., Feil, Y., & Johnson, A. R. (2007). An alternative reconceptualization of procedural and conceptual knowledge. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 38(2), 115–131.
Benecke, K., & Kaiser, G. (2023). Teachers’ approaches to handling student errors in mathematics classes. Asian Journal for Mathematics Education, 2(2), 161–182. https://doi.org/10.1177/27527263231184642
Blum, W., & Leiss, D. (2007). How do teachers deal with modelling in statistics lessons? In C. Haines, P. Galbraith, W. Blum, & S. Khan (Eds.), Mathematical modelling (ICTMA 12): Education, engineering and economics (pp. 133–144). Horwood Publishing.
BSKAP. (2024). Capaian pembelajaran pada pendidikan anak usia dini, jenjang pendidikan dasar, dan jenjang pendidikan menengah pada Kurikulum Merdeka. Jakarta: Kemdikbudristek.
Clarke, D., & Roche, A. (2018). Enhancing students’ understanding of exponential relationships through representations. Australian Mathematics Teacher, 74(2), 3–10.
Clarkson, P. (1991). Language comprehension errors: A further investigation. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 3(2), 24–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03217225
Diamond, A. (2013). Executive functions. Annual Review of Psychology, 64, 135–168. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750
Dinnullah, R. N. I., Noni, E., & Sumadji, S. (2019). Analisis kesalahan siswa pada penyelesaian soal cerita berdasarkan tahapan Newman. Jurnal Tadris Matematika, 2(2), 175–184. https://doi.org/10.21274/jtm.2019.2.2.175-184
Dwinata, A., & Febrian, F. (2018). Analisis kesalahan siswa dalam pemecahan problematika kaidah pencacahan titik sampel. Jurnal Gantang, 3(2), 121–129. https://doi.org/10.31629/jg.v3i2.479
Ericsson, K. A. (2008). Deliberate practice and the acquisition and maintenance of expert performance in medicine and related domains. Academic Medicine, 84(10 Suppl), S1–S11.
Fauzia, T. I., & Retnawati, H. (2023). Analisis kesalahan siswa SMA dalam mengerjakan soal literasi matematika model AKM. Jurnal Pedagogi Matematika, 9(2), 143–156. https://doi.org/10.21831/jpm.v9i2.19624
Flavell, J. H. (1976). Metacognitive aspects of problem solving. In L. B. Resnick (Ed.), The nature of intelligence (pp. 231–235). Lawrence Erlbaum. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781032646527-16
Geary, D. C. (2004). Mathematics and learning disabilities. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 37(1), 4–15. https://doi.org/10.1177/00222194040370010201
Gunawan, M. S., & Fitra, D. (2021). Kesulitan siswa dalam mengerjakan soal eksponen dan logaritma. Mosharafa: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 10(2), 257–268. https://doi.org/10.31980/mosharafa.v10i2.875
Hattie, J. (2009). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. Routledge.
Hidayanto, T., Subanji, S., & Hidayanto, E. (2017). Deskripsi kesalahan struktur berpikir siswa SMP dalam menyelesaikan masalah geometri serta defragmentingnya: Suatu studi kasus. Jurnal Kajian dan Pembelajaran Matematika, 1(1), 72–81.
Hiebert, J. (2013). Conceptual and procedural knowledge: The case of mathematics. In S. P. Lajoie (Ed.), Computers as cognitive tools: No more walls (pp. 381–398). Lawrence Erlbaum. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203063538
Jitendra, A. K., George, M. P., & Sood, S. (2019). Mathematical problem-solving: Errors, misconceptions, and strategies. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 52(6), 523–536.
Kazemi, F., & Rafiepour, A. (2015). Students’ difficulties in modeling exponential growth problems. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 46(7), 1058–1071.
Kramarski, B., & Mevarech, Z. (2003). Enhancing mathematical reasoning: Effects of metacognitive training on problem solving. American Educational Research Journal, 40(1), 281–310. https://doi.org/10.3102/00028312040001281
Mayer, R. E. (2009). Multimedia learning (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Miyake, A., Friedman, N. P., Emerson, M. J., Witzki, A. H., Howerter, A., & Wager, T. D. (2000). The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contributions to complex "frontal lobe" tasks: A latent variable analysis. Cognitive Psychology, 41(1), 49–100. https://doi.org/10.1006/cogp.1999.0734
Murtiyasa, B., & Wulandari, D. (2020). Analisis kesalahan siswa dalam menyelesaikan soal eksponen melalui pembelajaran online di masa pandemi kelas X SMA Swasta Tamansiswa Binjai. Serunai: Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu Pendidikan, 6(2), 86–91. https://doi.org/10.37755/sjip.v6i2.331
Newman, M. A. (1977). An analysis of sixth-grade pupils’ errors on written mathematical tasks. Victorian Institute for Educational Research Bulletin, 39, 31–43.
Nofrianto, A. (2022). Student errors in mathematics word problems: What can be learned? Jurnal Gantang, 7(1), 59–67. https://doi.org/10.31629/jg.v7i1.4426
Nurianti, E., & Ijudin, R. (2015). Analisis kesalahan siswa dalam menyelesaikan soal matematika materi pecahan bentuk aljabar di kelas VIII SMP. Jurnal Pendidikan dan Pembelajaran Khatulistiwa, 4(9).
Rahma, A. F., & Khabibah, S. (2022). Analisis kesalahan siswa SMA dalam menyelesaikan soal eksponen. MATHEdunesa, 11(2), 446–457. https://doi.org/10.26740/mathedunesa.v11n2.p446-457
Rahmawati, D., & Permata, L. D. (2018). Analisis kesalahan siswa dalam menyelesaikan soal cerita program linear dengan prosedur Newman. Jurnal Pembelajaran Matematika, 5(2). https://doi.org/10.30656/gauss.v2i1.1406
Resnick, L. B. (1992). From protoquantities to operators: Building mathematical competence on a foundation of everyday thinking. In G. Leinhardt, R. Putnam, & R. A. Hattrup (Eds.), Analysis of Arithmetic for Mathematics Teaching (pp. 373–429). Lawrence Erlbaum. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315044606-7
Ron, G., Dreyfus, T., & Hershkowitz, R. (2020). Students’ reasoning about exponential functions: A structural analysis. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 103, 155–176.
Rosyadi, A. A. P., Kafifah, A., Cholily, Y. M., & Inganah, S. (2024). Students’ mathematical errors in solving literacy and numeracy problems. JRAMathEdu (Journal of Research and Advances in Mathematics Education), 9(2), 105–116. https://doi.org/10.23917/jramathedu.v9i2.10464
Şenay, Ş. C. (2024). Analysis of misconceptions and errors regarding exponential and radical expressions through the theory of reducing abstraction. Research on Education and Psychology, 8(2), 281–295. https://doi.org/10.54535/rep.1520588
Siegler, R. S., & Stern, E. (1998). Conscious and unconscious strategy discoveries: A microgenetic analysis. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 127(4), 377–397. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.127.4.377
Stacey, K., & Vincent, J. (2009). Modes of reasoning in algebra. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 28(1), 1–12.
Star, J. R., & Stylianides, G. J. (2013). Procedural and conceptual knowledge: Exploring the relationship in mathematics. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 44(2), 238–248.
Susanti, W., & Kartini, K. (2024). Analisis kesalahan siswa Madrasah Aliyah dalam menyelesaikan soal materi eksponen berdasarkan prosedur Kastolan. El-Khuwailid: Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies, 1(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.63826/el-khuwailid.v1i1.1
Sweller, J., Ayres, P., & Kalyuga, S. (2011). Cognitive load theory in education: An overview. International Journal of Educational Research, 50(5–6), 431–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8126-4
Yodiatmana, Y., & Kartini, K. (2022). Analysis of student errors in solving basic logarithmic problems using Kastolan error analysis. Jurnal Gantang, 7(2), 129–136. https://doi.org/10.31629/jg.v7i2.4689
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Jurnal Gantang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.