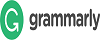The Effect of Welding Speed on the Welding Quality AISI 1020 and AISI 1050 Steel Using Shielded Metal Arc Welding Technology
Keywords:
SMAW welding, AISI 1020 steel, AISI 1050 steel, red dye penetrant test, Tensile and Impact testAbstract
Material joining techniques are divided into two categories: similar joints and dissimilar joints. The difference in thermal cycles experienced by each material is the reason why dissimilar welding is more challenging than similar welding. The welding process that joins two materials with different properties is commonly used to improve effectiveness and efficiency in production, as well as to improve product quality. This trend has become popular in the manufacturing industry, including in the manufacture of tailor welded blanks, transportation vehicle frames such as aircraft, trains, and cars, as well as in the manufacture of public and private vehicle accessories such as aircraft panels and exhausts. The materials currently widely used in exploration are stainless steel combined with carbon steel, as well as a mixture of stainless steel and low carbon steel, which is quite challenging to weld but offers the advantages of higher strength, corrosion resistance, and lighter weight. This challenge can be overcome through liquid welding methods, one of which is the "SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding)" technique. This study used variations in welding time at 5, 10, and 10 m/minute. Quality testing was carried out using visual tests, tensile tests, and impact tests, using AISI 1020 steel and AISI 1050 steel. Based on the test results, there was a significant difference in that the welds appeared to be shinier. The tensile strength results were in the form of average strain values for each specimen, which were 0.0705 mm, 0.0487 mm, and 0.1074 mm. The impact test results, which compared toughness values using a predetermined welding time variation of 16.5 joules, showed an average toughness value of 0.1948 J/mm².