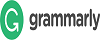Investigation of Electrical Voltage Influence on Thermoelectric Cooler (TEC) Performance in a Stacked Cooling Enclosure
Keywords:
Thermoelectric Cooler, electrical voltage, thermal performance, Coefficient of PerformanceAbstract
The Thermoelectric Cooler (TEC) is an environmentally friendly solid-state cooling technology with wide application potential. This study aims to analyze the effect of voltage variation on the thermal performance of a TEC-based cooling system applied to a prototype cooling box. The methodology involved designing a system with eight symmetrically installed TEC units, tested at five voltage levels: 16 V, 18 V, 20 V, 22 V, and 24 V. Evaluated parameters included cold and hot side temperatures, heat absorbed (Qc), and Coefficient of Performance (COP). Experimental results revealed that increasing voltage up to 22 V significantly enhanced system efficiency, with the highest COP of 0.25 and maximum Qc of 5.24 W. However, at 24 V, performance declined due to excessive heat accumulation on the hot side of the TEC, exceeding heat dissipation capacity. In conclusion, an optimal input voltage of 22 V was identified to yield the most efficient cooling performance. These findings support the applicability of TEC technology for compact and sustainable cooling systems.