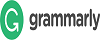The Influence of Adding Matos Soil Stabilizer to the Foundation Layer of a Road Body Stabilized Using Lime on it’s Physical Properties.
Abstract
From the perspective of Civil Engineering, soil is a collection of minerals, organic matter, and relatively loose deposits, which are located on bedrock. The relatively weak bonds between grains can be caused by carbonates, organic matter, or oxides precipitating between the particles. The space between the particles can contain water, air, or both. The process of physical soil formation that changes rock into smaller particles, occurs due to the effects of erosion, wind, water, humans, or the destruction of soil particles due to changes in temperature or weather. Soil stabilization with lime and matos soil stabilizer is an alternative soil improvement by adding additives. Soil stabilization with lime and matos soil stabilizer as a mixture of crushed soil, lime, matos soil stabilizer, and water which is then compacted to produce a new material, where strength, deformation characteristics, resistance to water, weather, and so on can be adjusted with the need for road pavement, building and road foundations, streams, retaining walls and so on.
The physical properties test used is water content (w), γ = soil volume weight (gr/cm3), specific gravity (Gs), atterberg limits, permeability, hydrometer and gradation analysis