Comparison Study Between the Experimental and Finite Element Analysis (FEA) on a Static Load of Magnesium AZ31B as Biodegradable Bone Plate Material
Keywords:
Magnesium AZ31B, bone plate, three point bending, FEAAbstract
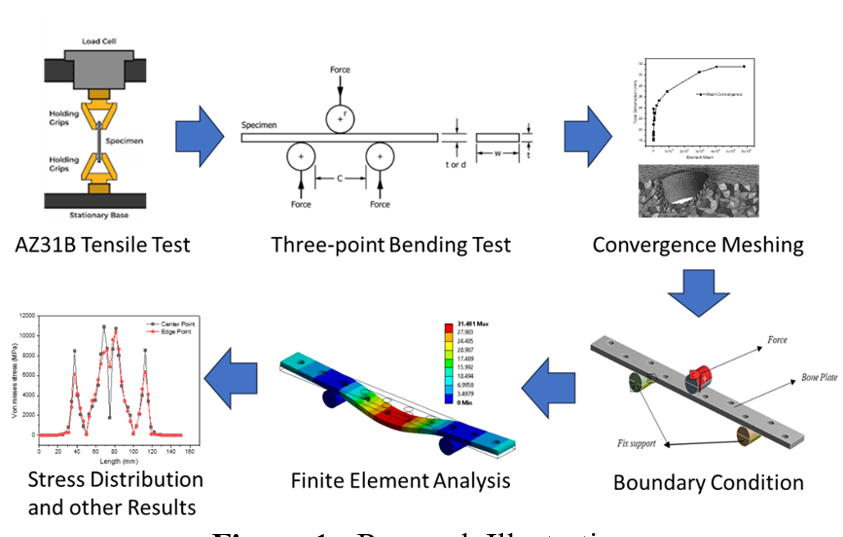
Biomaterials is an advanced material engineering technology that is used to help heal bone fractures or fractures. Currently, many biomaterials use materials such as titanium alloy, stainless steel, platinum, and chromium, but these materials cannot be degraded naturally so a second operation must be carried out to remove the installed biomaterial. Biomaterials are temporary in nature so when the bone returns to its original state, the biomaterial must be surgically removed. Research was conducted to obtain a design with a material that can be naturally degraded without causing toxicity. Magnesium AZ31B is a recommended candidate as a base material for degradable bone implants. Magnesium AZ31B material, it is expected to reduce or minimize the surgical removal of implant biomaterials. Bone plate geometry use plate bone dimension 150mm x 15mm x 3mm with variation 10 hole parallel and zigzag as well as with a bolt bone dimensions long 40 mm with pitch 1mm diameter 5mm. Test bending was conducted with ASTM E290-14 showing that on plate bone hole parallel with burden maximum 33,419 KN with a deformation maximum of 30.89 mm whereas for plate bone hole zig zag with the burden maximum 32,863 KN with deformation maximum big as 29.97 mm. From the study experimental that plate bone hole parallel have nature mechanic more tall compared with plate bone hole zig Zag although with the difference which is not significant. Whereas on simulation FEA plate bone hole parallel with burden 33,419 KN get results total deformation as big as 31,481 mm with von Mises stress 15,337 MPa, then for plate bone hole zig Zag with burden 32,863 KN with total deformation 32.466 mm and von Mises stress as big as 33,948 MPa. In testing by experiment and simulation FEA plate bone hole parallel get difference around 0.591 mm or 0.94% whereas for plate bone hole zig Zag in testing by experiment and simulation get difference around 2,893 mm or 4.60%.