Geological Structure Identification using Derivative Analysis of Gravity Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31629/jit.v3i2.5048Keywords:
gravity, Bouguer anomaly, structure geology, FHD, SVDAbstract
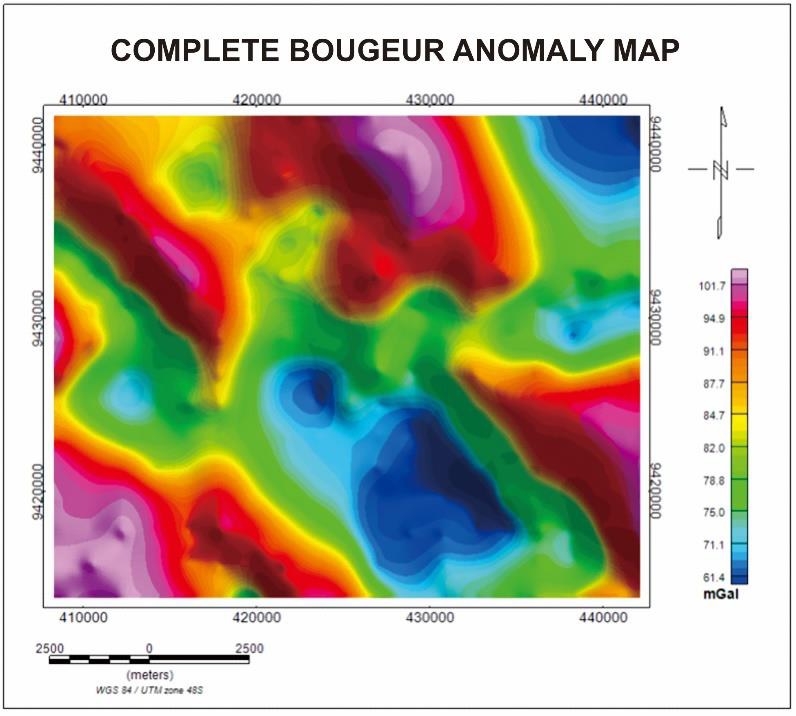
The gravity method is a geophysical method that can be used for exploration activities to identify subsurface geological structures through variations in the gravitational field due to differences in rock mass density below the surface based on measurements of variations in the earth's gravitational field. In this study, the gravity method was used to detect subsurface structures. The modeling is used to identify based on the gravity anomaly data that has been obtained and also see the structure of the regional geology of the area. The values ??depicted at the study site for the complete Bouguer anomaly range from 69.3 mGal to 95.5 mGal. The first horizontal derivative map of the research area shows the maximum value as the contact area or changes in the value of the anomaly caused by geological structures. Then the second vertical derivative map shows the 0-boundary plane identified by faults. In the analysis of the FHD curve, it shows that there is a maximum value that indicates the boundary of the contact area of ??the layer, and SVD shows a value that passes the zero limit so that it delivers the existence of a fault structure in the Suoh area of ??West Lampung.